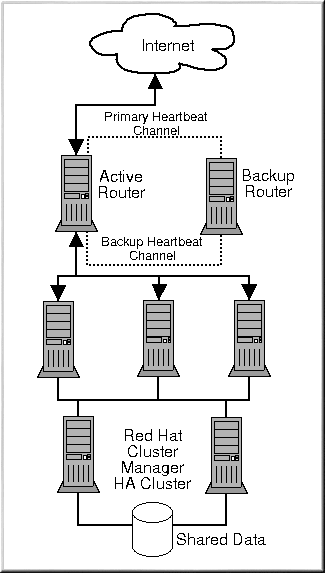
A Three Tiered LVS Configuration
Figure 6-2 shows a typical three tiered LVS cluster topology. In this example, the active LVS router routes the requests from the Internet to the pool of real servers. Each of the real servers then accesses a shared data source over the network.
This configuration is ideal for busy FTP servers, where accessible data is stored on a central, highly available server and accessed by each real server via an NFS exported directory or Samba share. This topography is also great for websites that access a central, highly available database for transactions. And using an active-active configuration with Red Hat Cluster Manager, the administrator can configure one high-availability cluster to serve both of these roles simultaneously.
The third tier in the above example does not have to use Red Hat Cluster Manager, but failing to use a highly available solution would introduce a critical single point of failure. For more information on setting up Red Hat Cluster Manager high availability cluster refer to the Red Hat Cluster Manager Installation and Administration Guide.